Dismiss
Innovation
A platform built for AI
Unified, automated, and ready to turn data into intelligence.
Dismiss
June 16-18, Las Vegas
Pure//Accelerate® 2026
Discover how to unlock the true value of your data.
Dismiss
NVIDIA GTC San Jose 2026
Experience the Everpure difference at GTC
March 16-19 | Booth #935
San Jose McEnery Convention Center
SAN vs. NAS vs. DAS: What’s the Difference?
Deciding on the right storage system can be a complex decision, as it needs to balance costs, storage capacity needs, and scalability requirements. The three primary options for enterprise data storage systems are direct-attached storage (DAS), network-attached storage (NAS), and storage area networks (SANs). Each offers advantages and disadvantages for organisations.
Here, we’ll look at the use cases, strengths, and weaknesses of each of these three storage systems to help you choose the one that best suits your business requirements.
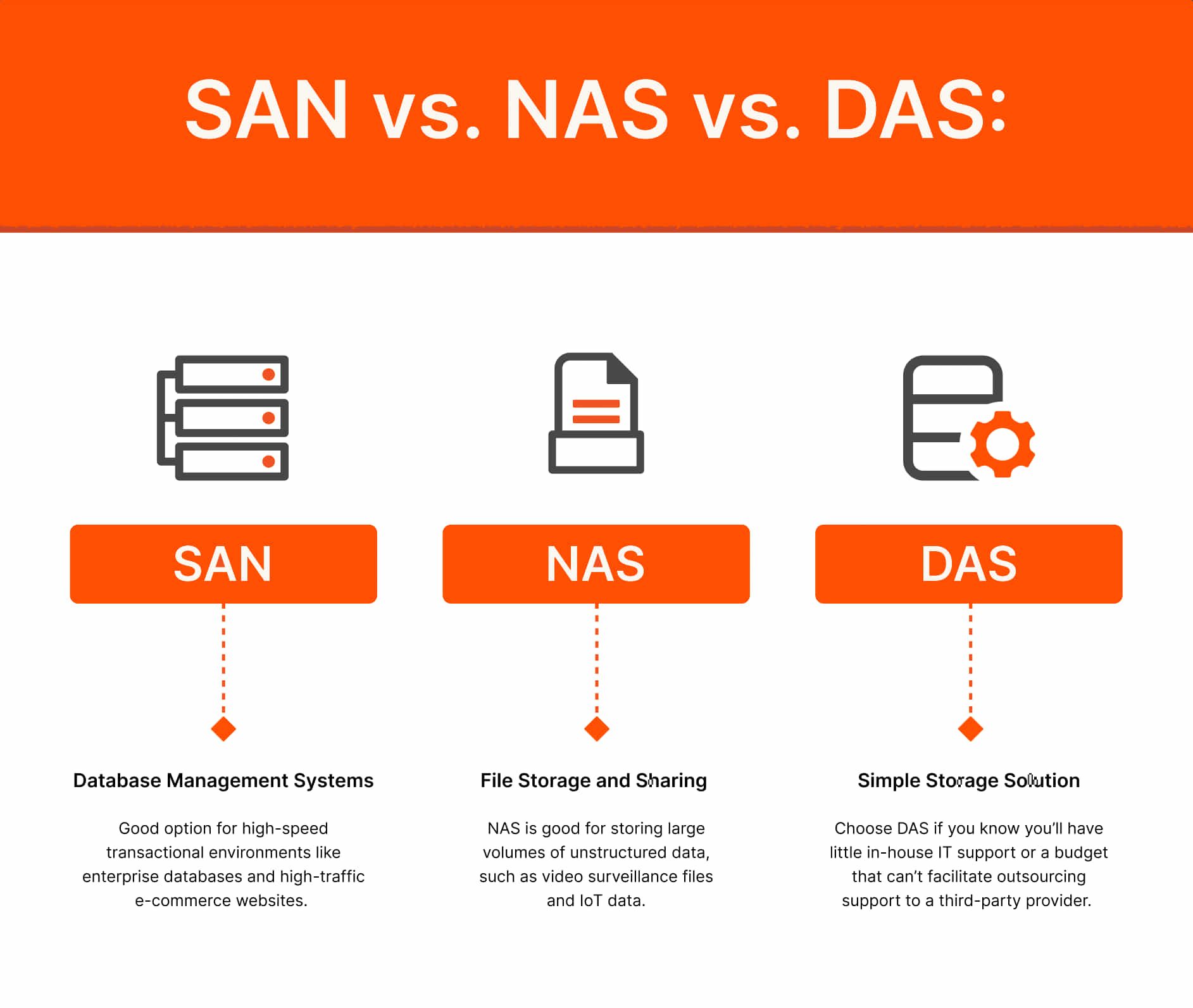
Where Do You Use SAN?
Database Management Systems
Databases often support mission-critical workloads that process large amounts of transactional data and may need to handle hundreds of thousands of transactions per second. This requires reliable, scalable storage that can deliver high input/output operations per second (IOPS) and low latency rates.
SANs deliver high I/O processing speeds and low latency for block storage, making them ideal for mission-critical databases and high-transaction environments. Modern SANs now leverage not only Fibre Channel but also IP-based protocols like iSCSI and, increasingly, NVMe over Fabrics (NVMe-oF), which deliver near-DAS performance and lower latency for flash storage.
Virtualisation and Modern Workloads
Virtualised environments require large-scale and high-performance deployments and often comprise thousands of virtual machines (VMs) running a wide range of operating systems and applications.
SANs can quickly transfer multiple I/O streams between VMs and virtualisation hosts, making them better suited than NAS for virtualised environments. And with NVMe-oF and unified storage platforms, SANs now support not just traditional VMs but also containerized and AI/ML workloads, providing the performance and flexibility required for next-generation applications.
Where Do You Use NAS?
File Storage, Collaboration, and Big Data
NAS remains the go-to for centralized file storage and sharing, supporting collaboration across diverse operating systems. Modern NAS solutions, such as Everpure FlashBlade®, now offer high availability, scale-out architectures, and support for both file and object protocols (NFS, SMB, S3), making them suitable for big data analytics, AI/ML, and unstructured data at scale.
High-performance and AI/ML Workloads
Today’s NAS platforms can deliver high throughput and low latency, supporting demanding workloads like AI training, genomics, and real-time analytics. Features like multi-gigabit connectivity, NVMe SSD caching, and integration with cloud-native tools have redefined NAS performance.
Where Do You Use DAS?
Simple, Localized Storage Needs
DAS is directly attached to a single server, offering simplicity and low cost. While still relevant for certain edge or single-server use cases, DAS is increasingly being replaced by shared storage solutions—even for small businesses—thanks to the affordability and simplicity of modern SAN and NAS platforms.
Modern Alternatives for Small Businesses
Everpure FlashArray™ and FlashBlade now offer entry-level models and subscription-based pricing, making enterprise-grade shared storage accessible to organisations of all sizes. This enables small businesses to benefit from features like centralized management, data protection, and cloud integration without the complexity or cost previously associated with SAN/NAS. Unified storage platforms like FlashArray and FlashBlade now blur the lines between SAN and NAS, offering block, file, and object storage on a single system with global data reduction, high availability, and seamless cloud integration.
NAS vs. SAN vs. DAS: What Are the Differences?
The major differences between DAS, NAS, and SAN are costs, scalability, and how storage is shared. The three systems also use different storage mechanisms: DAS primarily uses hard-drive storage with sectors, NAS uses shared files, and SAN uses block storage.
Different technologies are also used for transmitting data. DAS uses IDE/SCSI, NAS uses TCP/IP and Ethernet, and SAN uses Fibre Channel and IP.
NAS vs. SAN vs. DAS: What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages?
What Are the Advantages of SAN?
- SAN supports both Fibre Channel and modern IP-based protocols (iSCSI, NVMe-oF) for flexible, high-performance connectivity.
- Unified platforms enable block and file access, simplifying management and reducing silos.
- Cloud integration and hybrid deployments are now standard, supporting disaster recovery and workload mobility.
What Are the Disadvantages of SAN?
- Complexity and cost can be disadvantages, but cloud-based dashboards like Pure1® help reduce them through simplified management and subscription pricing.
- The initial setup may still require expertise, but unified management tools have lowered the barrier for this for smaller organisations.
What Are the Advantages of NAS?
- Modern NAS supports high availability, scale-out performance, and multi-protocol access (NFS, SMB, S3).
- Flash-based NAS (e.g., FlashBlade) delivers performance suitable for AI/ML, analytics, and high-throughput workloads.
- Cloud integration, hybrid storage, and object support are now common.
- No longer limited to small networks, modern NAS can serve enterprise and AI-scale needs.
What Are the Disadvantages of NAS?
Performance and availability limitations can sometimes be an issue, but those have been largely overcome with all-flash, scale-out architectures and advanced protocols.
What Are the Advantages of DAS?
- DAS offers simple, low-cost, and high performance for single-server use.
- Modern alternatives (entry-level FlashArray/FlashBlade) now offer similar simplicity with the benefits of shared storage, central management, and cloud integration.
What Are the Disadvantages of DAS?
- DAS has limited scalability.
- It isn’t recommended for organisations needing collaboration, data protection, or hybrid cloud capabilities.
Which Is Better? NAS vs. SAN vs. DAS
DAS, NAS, and SAN all offer benefits, but how meaningful they are for your organisation will depend on your needs. Ultimately, the best solution for you will come down to the amount of storage capacity you need, your budget, and your backup and disaster recovery requirements.
Will you need to add storage capacity in the near future? How many employees need to access storage at the same time? Will they need remote access? Do you have the IT resources to manage the chosen storage system? These are just some of the questions you’ll need to answer when choosing between NAS, SAN, and DAS.
If you’re a small business with limited financial and IT resources, DAS is likely your best option. But if you’re moving to a NAS or SAN solution for greater performance and higher storage capacity, Everpure provides several solutions that leverage the unique characteristics of all-flash storage:
- FlashBlade//S™ and FlashBlade//EXA™: Scale-out file and object storage for unstructured data, AI/ML, analytics, and high-performance computing. Supports NFS, SMB, S3, and S3-over-RDMA for accelerated AI workloads
- FlashArray//X™, FlashArray//C™, and FlashArray//XL™: Unified block and file storage with NVMe-oF support, high availability, and cloud integration. Suitable for databases, virtualisation, and operational workloads of all sizes
- Portworx®: Kubernetes-native storage for containerized and cloud-native applications, supporting AI/ML and hybrid cloud deployments
- Pure Fusion™: Unified data management across file, block, and object storage on premises and in the cloud
Whether you’re in need of a SAN or a NAS, the Everpure platform is here to help.
We Also Recommend...
Browse key resources and events

SAVE THE DATE
Pure//Accelerate® 2026
Save the date. June 16-19, 2026 | Resorts World Las Vegas
Mark your calendars. Registration opens in February.
PURE360 DEMOS
Explore, learn, and experience Everpure.
Access on-demand videos and demos to see what Everpure can do.

VIDEO
Watch: The value of an Enterprise Data Cloud
Charlie Giancarlo on why managing data—not storage—is the future. Discover how a unified approach transforms enterprise IT operations.
RESOURCE
Legacy storage can’t power the future
Modern workloads demand AI-ready speed, security, and scale. Is your stack ready?
Personalize for Me

