SAN の用途
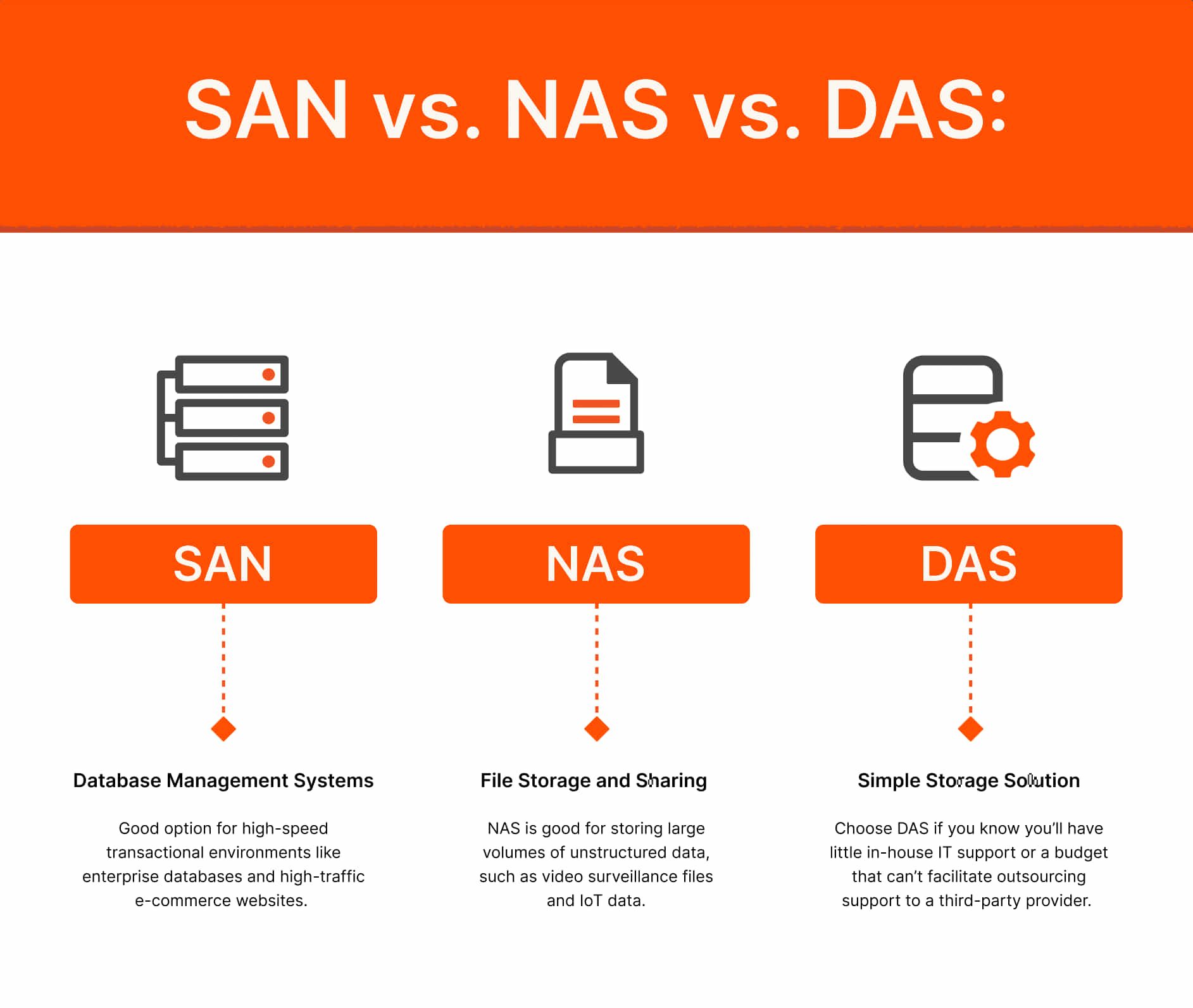
データベース管理システム
データベースは、大量のトランザクション・データを処理するミッション・クリティカルなワークロードをサポートすることが多く、1 秒あたり数十万件のトランザクションを処理する必要がある場合があります。これには、高い IOPS(1 秒あたりの入出力処理回数)と低レイテンシ―を提供できる、信頼性が高くスケーラブルなストレージが必要です。
SAN は、ブロック・ストレージに高い I/O 処理速度と低レイテンシ―を提供し、ミッション・クリティカルなデータベースやトランザクションの多い環境に最適です。モダンな SAN は、ファイバー・チャネルだけでなく、iSCSI などの IP ベースのプロトコルや、フラッシュ・ストレージにほぼ DAS の性能と低レイテンシ―を提供する NVMe over Fabrics(NVMe-oF)を活用しています。
仮想化とモダン・ワークロード
仮想化環境では、大規模で高性能な展開が必要であり、多くの場合、さまざまな OS やアプリケーションを実行する数千の仮想マシン(VM)で構成されます。
SAN は、VM と仮想化ホスト間で複数の I/O ストリームを迅速に転送できるため、仮想化環境では NAS よりも適しています。また、NVMe-oF と統合ストレージ・プラットフォームにより、SAN は従来の VM だけでなく、コンテナ化されたワークロードや AI/ML ワークロードもサポートし、次世代アプリケーションに必要な性能と柔軟性を提供します。
NAS の用途
ファイル・ストレージ、コラボレーション、ビッグデータ
NAS は、さまざまな OS 間のコラボレーションをサポートする、一元化されたファイル・ストレージと共有の頼れる存在です。ピュア・ストレージの FlashBlade などのモダンな NAS ソリューションは、高可用性、スケールアウト・アーキテクチャ、ファイル・プロトコルとオブジェクト・プロトコル(NFS、SMB、S3)のサポートを提供し、ビッグデータ分析、AI/ML、大規模な非構造化データに適しています。
高性能および AI/ML ワークロード
今日の NAS プラットフォームは、ハイスループットと低レイテンシ―を提供し、AI トレーニング、ゲノミクス、リアルタイム分析などの要求の厳しいワークロードをサポートします。マルチギガビット接続、NVMe SSD キャッシング、クラウドネイティブ・ツールとの統合などの機能により、NAS の性能が再定義されました。
DAS はどこで使われるのか
シンプルでローカルなストレージが必要な環境
DAS は単一のサーバーに直接接続されており、シンプルさと低コストを提供します。DAS は、エッジやシングル・サーバーの特定のユースケースに依然として適していますが、最新の SAN や NAS プラットフォームの手頃な価格とシンプルさのおかげで、小規模企業でも共有ストレージ・ソリューションに置き換えられつつあります。
中小企業向けのモダンな代替案
ピュア・ストレージの FlashArray と FlashBlade は、エントリーレベルのモデルとサブスクリプションベースの価格を提供し、エンタープライズグレードの共有ストレージをあらゆる規模の組織で利用できるようになりました。これにより、中小企業は、SAN/NAS に関連する複雑さやコストなしで、集中管理、データ保護、クラウド統合などの機能を利用できます。FlashArray や FlashBlade などの統合ストレージ・プラットフォームは、SAN と NAS 間の境界を曖昧にし、グローバルなデータ削減、高可用性、シームレスなクラウド統合により、ブロック、ファイル、オブジェクト・ストレージを単一のシステム上で提供します。
NAS、SAN、DAS:違い
DAS、NAS、SAN の主な違いは、コスト、スケーラビリティ、ストレージの共有方法です。3 つのシステムには、異なるストレージ・メカニズムも使用されています。DAS は主にセクターでハードドライブ・ストレージを使用し、NAS は共有ファイルを使用し、SAN はブロック・ストレージを使用します。
また、データ転送にはさまざまな技術が使用されています。DAS は IDE/SCSI、NAS は TCP/IP とイーサネット、SAN はファイバー・チャネルと IP を使用します。